
cAR is a camera application that leverages augmented reality technology to provide a real-time 3-D model of sports cars within the camera view of a user’s living room or garage. cAR allows users to create an account on the application, and pick any car from the internal database to view.
This document describes the software design and architecture of cAR application and is intended to allow any developer to reproduce the cAR application from scratch.
The cAR app is an iOS/Android application that was developed to generate AR videos of a car within a user’s camera application. The document is aimed at a developer with a background in Android and iOS development, who wishes to develop cAR from scratch.
The following common acronyms are used in this document. Any acronym not mentioned here will be present in the Data Dictionary.
Below is a comprehensive list of documents that were used as references to create the cAR software design document.
The SDD consists of a detailed description of cAR’s software architecture. This architecture can be classified into two categories, the frontend, and the backend.
The frontend and backend software architecture is described using UML diagrams. A data dictionary further elaborates and describes the purpose of each attribute and method found inside the respective class diagrams.
The user interface for the application is designed using two major tools: Adobe Xd for rapid prototyping, and the Google Flutter API for cross-platform uniform implementation. The layout and design of the interface are written in Dart, the language used by the Flutter API. This Dart code is then converted by the API into Swift and XML code for iOS devices, and Java/Kotlin and XML code for Android devices. The packages for each OS are then exported and made available for installation.
Due to the vast amount of screen size options available for Android devices, an explicit decision to render the UI for devices with an 18:9 aspect ratio screen is due to time constraints. This decision was made keeping in mind the fairly strenuous hardware requirements for running an AR application. Since almost all newer (and hence, more powerful and compatible) Android devices are available in an 18:9 aspect ratio, we have decided to target this screen ratio moving forward.
Initially, the project design proposal was to use two different database systems: Google Firebase API to manage user authentication and maintenance, and MySQL to manage the requirement of a Car database. Upon further investigation, it was found that the Firebase API proved a superior alternative for the database needs of the Car database as compared to MySQL. This was due to its ability to provide a cloud-based, easily updatable solution to entering new cars into the database, and the ability to use an offline version of the database in case network connectivity was unavailable, thus removing the possible need for an internet connection upon app reuse. Another advantage was the Flutter API providing in-built support for all Firebase features, significantly reducing the complexity of implementing any required database features. These advantages, combined with the reduced complexity of using only one database solution over two, led us to focus on using the Firebase API as our sole tool for both the User and Car databases while eliminating MySQL as a workflow tool.
The AR technical design was handled across two teams, iOS and Android. Both platforms require different implementations of the AR toolkit. On the iOS side, we plan on implementing the ARKit API, which combines the graphical capabilities of the SceneKit API to render 3D car models in a Camera scene. This API allows us to create powerful 3D AR renders using native iOS hardware without compromising performance. One limitation of ARKit is the lack of an available first-party implementation of a recording feature; this issue is resolved by using an external open-source implementation of this feature called SCNRecorder, which we list in Section 1.4.
On the AndroidOS side, we will use a similar implementation of the ARCore API designed by Google. ARCore also has a recording trigger built-in, so there is no inherent need for any external solutions, thus making ARCore a powerful self-contained system for not only displaying AR projections but also recording and reviewing them. As for the sharing and saving capabilities, Flutter allows us to implement a ‘Share’ functionality in our user interface, which provides a cross-platform solution to sharing or saving user recordings managed by the OS itself.
The front-end team is responsible for the development, implementation, and testing of the user interface and all responsive elements. A bottom-up approach will be used to develop the skeletal layout of the user interface using Dart with the Flutter API. Once the pre-designed prototype of the app is agreed upon, members of the front-end team will begin to integrate the app elements together to form a base for back-end integration.
Once the UI is developed, the back-end team will work with the front-end team to implement Firebase features into the pre-existing UI skeleton. This involves user authentication as well as the Car database features. Due to the strong flexibility of Flutter’s Firebase implementation, this step of the back-end process will not require platform-dependent development.
On the AR side, due to the platform dependency of the ARKit (iOS) and ARCore (AndroidOS) APIs, the implementation of the AR Camera projection features, as well as their recording capabilities, will be handled by separate iOS and Android teams. An effort will be made to use existing Flutter support for both iOS and AndroidOS AR APIs to simplify this process. However, due to limited support for this functionality, the majority of AR development will be done through Swift and Xcode on iOS and Kotlin and Android Studio for AndroidOS. To support parallel development, the AR team will use a static Car object to implement and develop AR features until the Firebase Car Database features can be integrated.
| Colour | Hex Code | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| 727272 |
|
|
| 7e7c7c |
|
|
| b9b9b9 |
|
|
| 182caf |
|
|
| 2544db |
|
|
| 4368c7 |
|
|
| 7c6eff |
|
|
| 7364ff |
|
|
| a39fff |
|
|
| d20000 |
|
|
| eb3939 |
|
|
| f0c418 |
|
|
| ffffff |
|
The main font used throughout the app will be Segoe UI and its derivatives, depending on the requirement for stronger cases such as bolding.

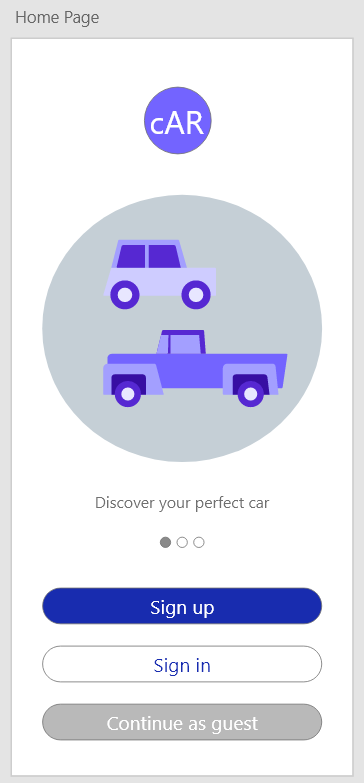
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| SignUpButton | Input Button | Links User to UserRegistrationView |
| SignInButton | Input Button | Links User to UserAuthenticationView |
| GuestButton | Input Button | Links User to CarListView |
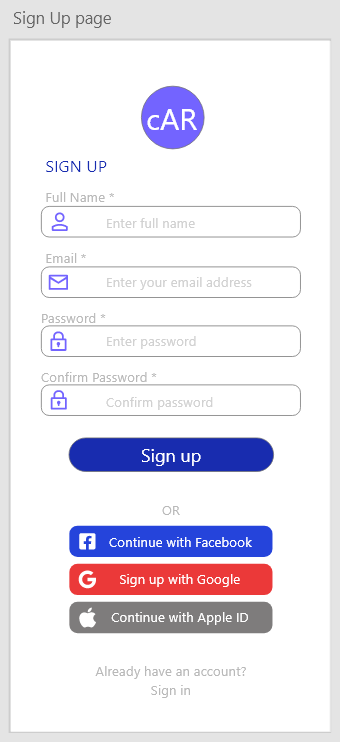
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| FullName | Input Text | Name of User |
| EmailCreation | Input Text | Email used for login |
| PasswordCreation | Input Password | Password for the account |
| ConfirmPassword | Input Password | Confirm Password |
| SignUpButton | Input Button | Links User to CarListView |
| FacebookSignUp | Input Button | Links User to Facebook for sign up |
| GoogleSignUp | Input Button | Links User to Google for sign up |
| AppleIdSignUp | Input Button | Links User to Apple for sign up |
| SignInButton | Input Button | Links User to UserAuthenticationView |
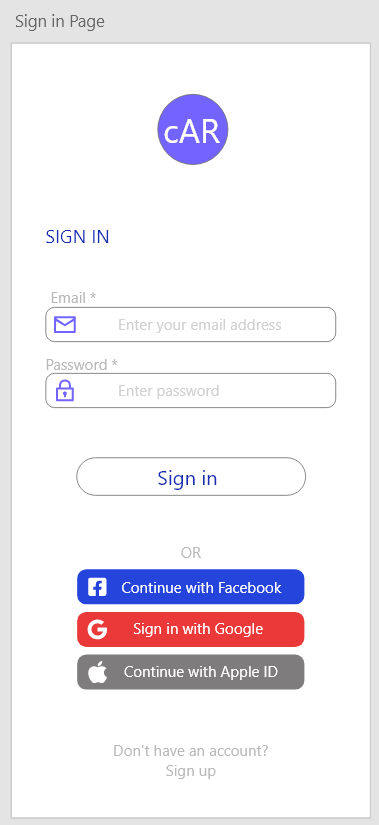
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Input Text | Email of an existing account | |
| Password | Input Password | Password for existing account |
| SignInButton | Input Button | Links User to CarListView |
| FacebookSignIn | Input Button | Links User to Facebook for sign in |
| GoogleSignIn | Input Button | Links User to Google for sign in |
| AppleIdSignIn | Input Button | Links User to Apple for sign up |
| SignUpButton | Input Button | Links User to UserRegistrationView |
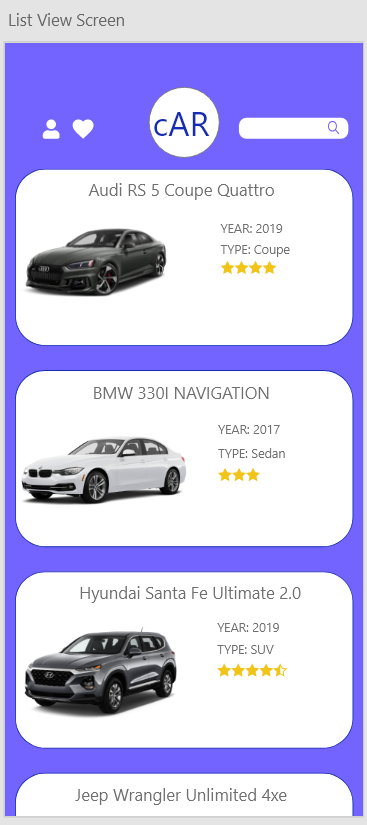
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| FavouritesButton | Input Button | Filters the list of Cars depending on favourites |
| SettingsButton | Input Button | Links User to UserSettingsView |
| CarButton | Input Button | Links User to DetailedCarView |
| Search | Input Text | Filters the list of Cars depending on search result |
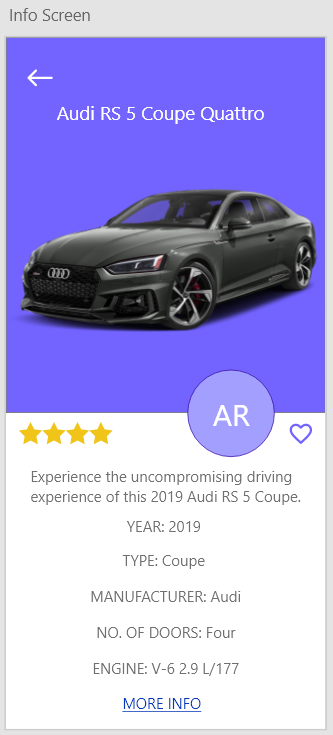
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ReturnButton | Input Button | Links User to CarListView |
| MoreInfoButton | Input Button | Shows the User more info about the chosen car |
| AddtoFavouritesButton | Input Button | Adds the car to the Users favourites |
| ARviewButton | Input Button | Links the User to ARCamView |

| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| RecordButton | Input Button | Starts the camera and records a video |
| SoundButton | Input Button | Mutes and unmutes sound |
| ReturnButton | Input Button | Links the User to DetailedCareView |
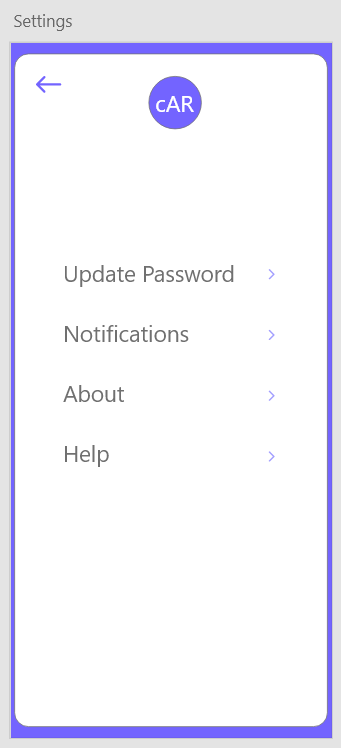
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ReturnButton | Input Button | Links User to CarListView |
| UpdatePassword | Input Button | Give User the option to update their password |
| NotificationsButton | Input Button | Allows User to modify their notification settings |
| AboutButton | Input Button | Allows User to see description of cAR |
| HelpButton | Input Button | Allows User to contact a developer for help |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ExitButton | Input Button | Links User back to DetailedCarView |
| EllipsisButton | Input Button | Give the user the option to open the page in another browser, copy or share the link |
| RefreshButton | Input Button | Gives the user a chance to refresh the page |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ReturnButton | Input Button | Links User back to DetailedCarView |
| AddAudioButton | Input Button | Give the user the option to add audio to the video |
| SaveButton | Input Button | Gives the user a chance to save the recording |
| ShareButton | Input Button | Lets the user share video directly from the app |
Document: Talal Elagha, Zhenyang Ding, Hussain Phalasiya, Omoma Eriamiantor, Lovette Oyewole, Abhirup Das, Matthew McBurnie, Jordan Den Hoed
Diagram: Lovette Oyewole, Zhenyang Ding, Hussain Phalasiya, Omoma Eriamiantor